
First, you need to find reliable manufacturers who can provide you with quality products. There are many Prefabricated House builders out there, so take the time to do your research and find one you trust.
Once you have found a manufactured home manufacturer, you need to decide what type of home you want. There are many different styles and designs, so take the time to browse the options and see what appeals to you.
The concept of prefabrication in construction corresponds to elements, parts or entire buildings that are manufactured in the factory and transported to a construction site for rapid installation.
It offers many advantages over traditional construction methods, such as speed, the precision of execution, efficiency, cleanliness of work and, in many cases, cost.
Housing is a primary human need, and the use of industrial methods to build affordable and quality housing has always interested architects, whether to accommodate growing urban populations or for temporary or emergency placements, at the lowest scales. more diverse.
After many attempts throughout history, the question remains whether the popularization of prefabs in the construction industry can be a solution to providing greater housing equity.
What is a prefabricated housing system?
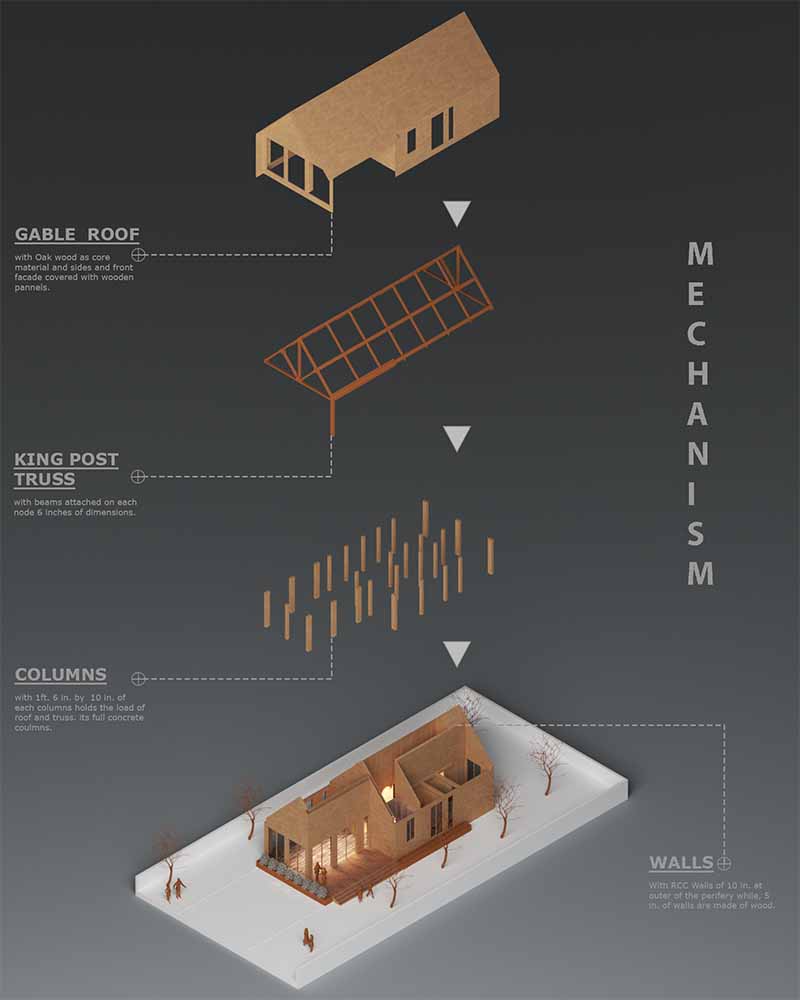
The concept of Prefabricated Homes in construction corresponds to elements, parts or entire buildings that are manufactured in the factory and transported to a construction site for rapid installation.
It offers many advantages over traditional construction methods, such as speed, the precision of execution, efficiency, cleanliness of work and, in many cases, cost.
Prefabricated Homes being a primary human need, architects have always had a passion for building affordable, quality housing using industrial methods, whether for growing urban populations or temporary or emergency settlements of all sizes. ‘interest.
After many attempts throughout history, the question remains whether the popularization of prefabs in the construction industry can be a solution to providing greater housing equity.
What are the principles and history of prefabrication?
Prefabrication is the practice of assembling structural components in a factory or other manufacturing site and transporting the complete assembly or subassembly to the construction site where the structure is located.
The term is used to distinguish this process from the more traditional construction practice of transporting basic materials to the construction site where all assembly takes place.
The term Prefabricated Homes also applies to the manufacture of something other than a structure in a fixed location. It is often used when the manufacturing of a part of a machine or any moving structure is moved from the main manufacturing location to another location and the parts are assembled and ready to be installed.
It is generally not used to refer to the electrical or electronic components of a machine, or the mechanical components such as pumps, gearboxes and compressors which are often supplied as separate items but to refer to the machine body parts that have been manufactured in the past. with the whole machine.
Prefabricated Homes parts of the machine body can be referred to as “sub-assemblies” to distinguish them from other assemblies. Prefabs have been used since ancient times.
For example, the oldest known man-made road in the world, the Sweet Track built in England around 3800 BC, is said to have been brought to the site using pre-fabricated segments of timber rather than being assembled on site.
The Sinhalese kings of ancient Sri Lanka used prefabricated building techniques to construct megastructures dating back to 2000, some of which were individually prepared and then assembled, notably in the fertile kingdoms of Anuradhapura and Polonnaruwa.
After the Lisbon earthquake of 1755, the Portuguese capital, in particular the Baixa district, was rebuilt on an unprecedented scale using prefabricated elements. Under Sebastião José de Carvalho e Melo, commonly known as the Marquis of Pombal, was D. Jose I, a new style of Pombalin architecture and urban planning emerged.
Introducing the first seismic design features and innovative prefabricated construction methods, with large multi-storey buildings fabricated entirely outside the city, transported in blocks, and then assembled on site.
This process continued into the 19th century, providing townspeople with new, safe buildings unheard of before the earthquake. Also in Portugal, the town of Vila Real de Santo António in the Algarve was founded on December 30, 1773, and was quickly built using prefabricated and quality materials.
The first prefabricated stone was laid in March 1774. On May 13, 1776, the city centre was completed and officially opened. In Australia in the 19th century, a large number of prefabricated houses were imported from Great Britain.
How are prefabricated houses constructed?
Drafting a Budget
Many people think that manufactured homes come from the manufacturer, fully finished and ready to move into. In reality, only a few producers can provide this service, and the vast majority will just provide you with housing and get it. Install on the base you provide.
Let’s see them in detail…
Earthworks and foundations: These are generally outside the scope of the manufacturer’s work and you must take care of them before the delivery of the house.
Connection: Same as above. The connection to the network (water, sewer, electricity, communication, etc.) will be planned and carried out at the same time as the foundation work.
Dwelling structure: from the manufacturer, generally installed and finished on the outside. Doors and Windows: Usually supplied and installed by the manufacturer…but be sure to clean up beforehand.
Roof: It depends on the type of roof you choose. Stone roofs are often excluded from the manufacturer’s scope of work due to shipping issues. If so, who will supply and install the tiles? …who will supply and install the wooden battens for the roof tiles?
Technical installations: Heating, electricity, ventilation, and plumbing are the main installations of the house and must generally be carried out by approved local companies. This means you will need to get a quote for these installations and work with the many companies that offer services once the house is complete.
Interior finishing: Once the technology is in place, the house is ready to be finished. Don’t just think about paint jobs… Things like interior doors, stairs, floors, flooring, window treatments…they have to be supplied and installed by someone. You must define “who did what and for how much” from the start.
Construction site: Last but not least… Accessibility, safety, and security are the most important things for a construction site. The site must be controlled.
Choosing other Contractors
The best practice for building a “do it yourself” home is to have the local general contractor do most of the work not done by the manufacturer (all concrete work, roofing, and interior finishing). When you hire a general contractor, you can be sure that the chances of error in the project will be minimized.
You also relieve the manufacturer a lot, which makes collaboration easier. Indeed, when it comes to general contractors, the builder has a competent point of contact on the site and the flow of information is fast, reliable and very efficient.
Don’t forget that in construction, a good flow of information is often the key to the success or failure of a project. For technical installations, it is recommended to negotiate with a professional company to choose a company that can provide a good technical solution at a competitive price. This will keep costs to a minimum while raising the quality to the best level you can afford.
Engineering Design
Once all parties involved have signed the contract, it is time to begin the technical design for the construction of the house. This step takes a lot of time and is one of the basic steps in building a prefabricated house. Depending on the size of the house and the complexity of the construction, the engineering can take from 4 to 12 weeks.
At this stage, the house is broken down into its basic components…like in a 3D puzzle. Then carefully design each component. When designing home components, designers should consider the layout of electrical, ventilation, and plumbing fixtures. For this reason, it is important to finalize agreements with all relevant companies before engineering design begins.
At the end of this phase, the complete set of drawings is ready to be manufactured. The designer will also prepare an installation manual for assembly on site, as well as a “basic load plan”.
Preparing the Site
Along with the technical design, the construction site will also be prepared. Before the design is completely completed, the manufacturer sends the load plan to the “Foundation Load Plan” so that the general contractor can carry out the foundation work. Needless to say, good timing is very important at this stage.
When the foundation has been poured and its measurements confirmed by the manufacturer, production can begin. If the final size/shape of the foundation (for whatever reason) differs from the design given by the manufacturer, immediate action should be taken to correct the error.
The general contractor will modify the foundation or the manufacturer will modify the design before production. Additional costs and damages for such errors will be collected by the general contractor who carried out the foundation work (be sure to state this clearly in your contract).
At this stage, you should also ensure that access to the site is clear so that haul trucks can reach the foundation slab.
Production
Production is one of the shortest steps in the whole process (transportation is the shortest). It takes less than a week to produce a custom one-room house. In the case of townhouses, a unit can be produced in 2-3 days. It’s very fast. To do this without a hitch, the engineering must be flawless.
This is why so much effort and time go into the design phase. The exceptional attention to detail is one of the things that set a manufactured home apart from a site-built structure. Good design and skilful execution result in high-quality components delivered to the Jobsite.
Transport
Once manufactured, the house is shipped to the construction site.
On-site Assembly
Finally, the house is assembled on site. The time nonelective for assembly varies depending on the level of construction and the size of the house. A modular single-family home can be assembled in a matter of days, while a similar house made with elements can take a week.
Manufacturers usually provide on-site assembly services and they require buyers to provide housing for their team (usually 4-5 workers per house).
The buyer also had to provide a crane to lower and lift the elements into place, as well as provide the necessary scaffolding to carry out the assembly and exterior finishing work. Cranes and scaffolding are relatively easy to install.
If you choose to hire a general contractor, you should already be covered and have nothing to worry about as they will handle all the on-site operations.
Technical Installations
Once the structure of the house has been built, the builder’s assembly team will leave and the site will be handed over to the general contractor, who will coordinate the work of the company that carries out the technical installation. Typical installations include plumbing, electrical, ventilation, heating and communications.
It may take a few weeks for all of this to be done and for the appropriate tests to be carried out. Ensuring that technical installations are carried out over a long time is the main reason why a manufacturer’s assembly team leaves without interior fittings.
Interior Finishes
In the final phase, the general contractor (or other mandated company) will carry out the interior renovation work. This phase can last from two weeks to several months, depending on the size of the house and the level of renovation.
It is important not to rush and do the finishing work carefully. Indeed, even if the structure of a house is perfect, poor finishes can lead to cracks in the walls and other unpleasant surprises.
Handing Over the House
Once the interior is complete, the general contractor will carry out a final inspection with the owner, who will have to check that everything is built according to plan and expectations.
#Make sure all steps will be performed after the finalisation of the final drawings.
Information Courtsey- Katus
How long does it take to build a prefab home?
Depending on the size and finish of the prefab, you can build a home in as little as three months. Most prefab homes can be built from start to finish in four to six months. This is much faster than traditional home construction, which takes around 8 months on average, and in some markets, custom home construction can take years.
Building most components in a factory limits weather delays, increases construction efficiency, and creates predictable delivery dates. You also don’t have change orders or as many work schedule conflicts. That said, the pre-licensing process can be lengthy in some regions, which is in addition to the estimated time above.
What are the types of prefabricated construction systems?
1. Panelized Wood Framing
Often used for roofs, these are long laminated timber frames covered with plywood or some type of clapboard roof. With panel frames up to 72 feet long, these roof panels save construction time and make roof construction safer.
2. Sandwich Panels
Made from 2 thin-facing materials such as concrete, plywood or stainless steel. The cover is then attached to an insulating core, usually made of a material such as foam, paper, fabric or rubber.
3. Steel Framing
Steel has been a popular and reliable building material in commercial and residential construction for centuries. Steel framing uses this strong and durable material to create pre-fabricated panels that can be used to construct buildings.
4. Timber Framing
Uncommon in India, timber frame panels are popular in other countries where timber houses are common. The frames are built at the factory and then used to build the wooden house.
5. Concrete Systems
Casting concrete chips for factory-built buildings offers more versatility and also saves time. Although building elements such as concrete slabs are heavier than other building elements, they are generally stronger and can improve the aesthetics of a building.
6. Modular Systems
These systems use all pre-engineered styles and create entire building structures typically made from pre-engineered units. The buildings are transported to the final construction site and then simply attached to the prepared foundations. Prefabrication requires architects, builders and suppliers to collaborate on the dimensions and specifications of the basic modular unit.
Information Courtsey- Go smart brick
What are the uses of prefabrication in construction?
- The maximum broadly used form of prefabrication in construction and civil engineering is the usage of Prefabricated Concrete.
- Casting the concrete step in the manufacturing cell brings the advantage of mould reuse, and the concrete pods can be assembled immediately without the need to transport them to congested production sites and pumps wet.
- The prefabricated strategy is to produce apartment pants and wood in housing elements with repeating housing units.
- Precast bridge elements and systems offer bridge designers and contractors significant advantages in terms of construction time, safety, environmental impact, construction liability and cost.
- After being manufactured in different countries or states from the final assembly site, prefabs are widely used in the assembly of aircraft and spacecraft with components such as wings and fuselage sections
What are some advantages and disadvantages of prefabrication?
Advantages
- Moving partial assemblies from a factory often costs less than moving pre-production resources to each site
- Deploying resources on-site can add costs; prefabricating assemblies can save costs by reducing on-site work
- Factory tools – jigs, cranes, conveyors, etc. – can make production faster and more precise
- Factory tools – shake tables, hydraulic testers, etc. – can offer added quality assurance
- Consistent indoor environments of factories eliminate most impacts of weather on production
- Cranes and reusable factory supports can allow shapes and sequences without expensive on-site falsework
- Higher-precision factory tools can aid the more controlled movement of building heat and air, for lower energy consumption and healthier buildings
- Factory production can facilitate more optimal materials usage, recycling, noise capture, dust capture, etc.
- Machine-mediated parts movement and freedom from wind and rain can improve construction safety
Disadvantages
- Transportation costs may be higher for voluminous prefabricated sections (especially sections so big that they constitute oversize loads requiring special signage, escort vehicles, and temporary road closures) than for their constituent materials, which can often be packed more densely and are more likely to fit onto standard-sized vehicles.
- Large prefabricated sections may require heavy-duty cranes and precision measurement and handling to place in position.
Information Courtsey- Wikipedia
What are some challenges of prefabrication?
- The design companies in the dossier are known to benefit greatly from prefab construction, with 80% or more of architects and engineers stating that prefab increases hard work productivity, reduces waste, will increase program certainty and improve quality.
Additionally, 75% report greater customer satisfaction and 78% report greater cost predictability. However, if the missions are not always designed to allow prefab, they will not get coins in their financial savings. As a documentation factor, “this should be a solid message that they want to extend the layout answer to make it more successful”.
- Delivery technology and type of business is a difficult situation for architects, engineers, fashion entrepreneurs/facility managers and industries – essentially all types of survey respondents. Premade strategies aren’t used much these days because they’re not standard anymore.
As the precast movement in the architecture mainstream grows, larger precast mechanical components and electrical content materials can be developed for larger, style-specific projects.
- While design firms cite lack of accessibility and skilled labour as major concerns, general contractors, contract managers and industry report that they don’t encounter barriers in these situations.
Respondents from the tech industry are the group that cares the least about whether or not homeowners want prefabs. Many mechanical, plumbing and some electrical contractors use prefabs, whether the homeowner specifies it or not.
Companies that recognize the inherent cost savings of prefab use it as an internal business practice, whether encouraged or not. Respondents who already use prefab said they would continue to use these processes “whether or not the owner agrees or is aware of it”.
- Survey participants identified benefits that they believe will lead to more prefabs in the future. These include, in order of impact: improving schedule performance, reducing construction costs, improving project quality, addressing labour shortages, and improving project security.
How is prefabrication changing the way mass housing is built?
According to industry reports, India’s urban housing shortage is estimated at 18.8 million units. Thus, as a solution, it is possible to use prefabrication technology to triple the speed of construction of the house. Multi-story buildings can now be constructed in 90 days and will require 20% fewer materials and space than traditional construction methods.
According to the prefab construction market report, the industry is expected to reach USD 135.9456 billion by 2023. The global prefab building market is set to grow rapidly and the commercial sector is currently dominating.
The advantage of a prefabricated house is that it significantly reduces construction time and is durable. Because these parts are manufactured in a controlled environment, they provide environmental benefits such as site safety, waste management, improved air quality, and quality management.
Prefabrication is an innovative construction technique that saves time and space. New technologies can be applied to precast hollow core panels and hollow walls, which are lighter, easier to install and have a longer service life.
Prefab is one the most effective and affordable. Some parts of prefabricated houses are not built on-site by carpenters but are mass-produced externally and shipped to the site at a much lower cost. In addition to being economical, prefabricated homes, also called modular homes, are safer than traditional homes. They are more resistant to natural disasters such as earthquakes or tsunamis.
Since most of the process is computerized in precast technology, human error is minimal. With proper planning, the number of vehicles and equipment required on a construction site can be reduced. Prefab homes are flexible enough to be easily disassembled and moved or rebuilt for reuse. It is also durable which is a bonus.
Prefab contributes to greener construction. Environmentally friendly buildings can be designed and constructed using this method. According to a survey, prefabricated homes have many potential advantages over site-built projects due to less waste on-site. Building in a safe environment ensures better insulation, precise sizing and connections, reducing the overall energy consumption of the house.
Although the initial cost of using prefabs may be higher, there are overall benefits. Faster execution and just-in-time delivery of the final product benefit developers and customers. Shoppers also have a variety of designs and styles to choose from. However, prefabricated houses also have certain disadvantages. Prefabrication requires skilled labour because the house must be assembled with precision.
Improper assembly can lead to problems such as broken seals and leaks. Since most construction work requires on-site adjustments, prefabrication limits the options for modifying the scope of building design. Shipping costs are also high. Lack of land is an obstacle. Many prefab apartments are built on demolished sites or extensions of existing homes. Prefab requires well-serviced land to be successful.
To build a manufactured home, the buyer must pay the manufacturer during construction. Also, many people consider manufactured homes to be low-income, low-quality homes that are extremely difficult to resell. While better financing for prefab developers seems to be guaranteed, banks aren’t as keen on smaller customers right now.
How prefabrication construction is different from modular construction?
| PREFABRICATION CONSTRUCTION | MODULAR CONSTRUCTION |
| Prefabricated or pre-engineered structural construction refers to the creation of pre-engineered panels and modules in a controlled, factory-like environment. Pre-engineered construction is one of the most popular forms of commercial construction. This is considered an environmentally friendly method of construction, as the waste from these modules is recycled at the factory itself. There is no interruption of work because the structures are manufactured in the factory. Prefab buildings take less time to construct than traditional buildings. Therefore, it is also a cost-effective form of construction. | The construction of modular buildings is mainly done in factories. The modules are then shipped and assembled on site. These modules are box-shaped structural units that when put together form the whole structure. The construction of modular buildings is mainly done in factories. The modules are then shipped and assembled on site. These modules are box-shaped structural units that when put together form the whole structure. Modular structural construction uses an inside-out approach to producing buildings. The modular frame is built horizontally, installed like a box, and then finished from the inside out. Modular buildings are one of the most commonly used forms of construction today because they take less time and are more cost-effective than traditional alternatives. |
Future of Prefabrication
As the advantages outweigh the disadvantages, prefabricated houses can be a successful construction model in developing economies like India. There is an old idea that prefab homes are poorly designed, but new developments may change and open up the market further. Many companies use prefabrication as it is an important strategy to advance in the construction industry.
The growing interest in this type of construction in India has led to the entry of global manufacturers of machinery and prefabricated parts into the country. There is an immediate need for more local industry players to actively participate in the manufactured housing paradigm and raise awareness among the general public.
Prefab technology plays a unique role in the Indian real estate industry and can take it to the next level. All of this will redefine the future of Indian real estate.
FAQs related to Prefabrication Construction
Are prefabricated houses cheaper?
Finally, manufactured homes are often more affordable than traditional homes, making them a great option for first-time home buyers or those looking to save money on a new home.
How long does a prefab house last?
Finally, manufactured homes are often more affordable than traditional homes, making them a great option for first-time home buyers or those looking to save money on a new home. But these are just numbers to assume… Something It’s being observed that most of the house survived more than ten years. This is because of the maintenance of the house from time to time.
Information Courtsey- Wikipedia, Archdaily
Hope you like our Article, Thank you.
For more Articles like that, please click on
Architects design a suspended city model around Burj Khalifa. What great news!
